Introduction
Imagine trying to have a conversation without a language — impossible, right? In the digital world, networking is that language. It connects devices, people, and systems, allowing data to flow seamlessly around the globe.
From streaming your favorite show to sending an email or running a business website, networking is the invisible magic behind the scenes. Whether you’re a student, an IT beginner, or a curious professional, understanding networking basics will help you unlock how today’s digital world functions.
What Is Networking?
Networking refers to the practice of connecting computers, devices, and systems to share information and resources. It involves hardware like routers and switches, and software that manages data transfer, security, and communication protocols.
Simply put:
Networking allows devices to talk to each other and work together efficiently.
Key Components of Networking
To understand networking, it helps to know its essential building blocks:
1. Network Types
Types of computer networks, LAN vs WAN, network types explained
- LAN (Local Area Network): Connects devices in a small area like a home, office, or school.
- WAN (Wide Area Network): Connects larger areas, like cities or countries — the internet is the biggest WAN.
- MAN (Metropolitan Area Network): Covers a city or campus-sized area.
- PAN (Personal Area Network): Connects personal devices close to one person (like Bluetooth headphones and smartphones).
2. Networking Devices
- Router: Directs traffic between different networks, like your home Wi-Fi router.
- Switch: Connects devices within the same network, helping them communicate faster.
- Modem: Converts internet signals to your home network.
- Access Point: Extends wireless network coverage.
3. Networking Protocols
Networking protocols explained, common network protocols include:
- TCP/IP (Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol): The foundation of the internet.
- HTTP/HTTPS: Protocols for web browsing.
- FTP: Transfers files between computers.
- DNS (Domain Name System): Translates website names into IP addresses.
4. IP Addressing
Every device on a network needs an address called an IP address to identify itself and send/receive data. what is an IP address, IPv4 vs IPv6
There are two main types:
- IPv4: The traditional address format (e.g., 192.168.1.1)
- IPv6: The new, expanded format designed to solve the shortage of IPv4 addresses.
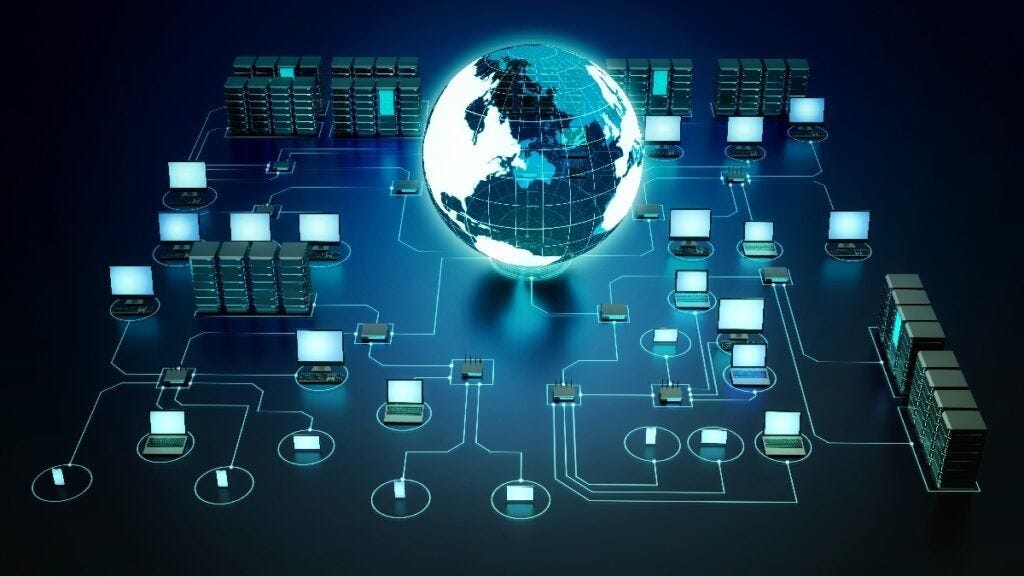
How Networking Powers the Internet
The internet is a massive global network — a network of networks. Without networking, websites, online services, and apps simply wouldn’t exist. How does the internet work, networking and the internet
Here’s how networking makes it all possible:
- Data packets: Information is broken down into packets that travel independently across networks.
- Routers and switches: These devices direct packets to their destination.
- Servers: Powerful computers that store websites, files, and applications.
Common Networking Technologies
- Wi-Fi: Wireless networking technology that connects devices without cables.
- Ethernet: Wired connection standard known for speed and reliability.
- VPN (Virtual Private Network): Creates a secure connection over the internet for privacy and remote access.
- Cloud Networking: Uses internet-based resources to build flexible and scalable networks.
Networking Security: Protecting Your Data
Security is a top priority in networking. Threats like hacking, malware, and data breaches are real, so networks need protection layers. network security basics, how to secure a network, firewall explained
- Firewalls: Block unauthorized access.
- Encryption: Scrambles data so only authorized users can read it.
- Antivirus software: Detects and removes malicious programs.
- Strong passwords and two-factor authentication: Prevent unauthorized logins.
The Role of Networking Professionals
Networking specialists design, build, and maintain these complex systems network engineer job description, careers in networking. Their tasks include:
- Installing and configuring network devices
- Monitoring network performance
- Troubleshooting connectivity issues
- Implementing security protocols
- Planning network upgrades
If you’re interested in a career in IT, network engineering is a growing, rewarding field.
Final Thoughts: Networking Is the Digital Lifeline
In today’s hyper-connected world, networking is essential. It links devices, powers the internet, and keeps businesses and people connected.
Whether you want to improve your personal tech skills or start a career in IT, learning networking basics is a smart, future-proof move.



Comments are closed